How to Upgrade Your Computer's Storage Capacity.
❤ 1% Better Every Day!
Learn one topic every day!
Thanks to ChatGPT and my colleagues, I have learned and gained a better understanding of concepts like RAM and SSD.
The differences between RAM and SSD.
How to upgrade RAM and SSD for a computer. ^_^
This curiosity for self-learning was sparked by the following image: (I took a photo and uploaded it to ask ChatGPT to analyze the circuit board as noted)
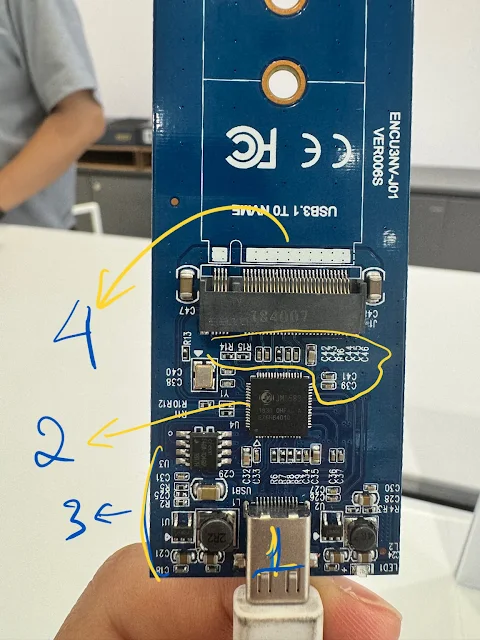 |
| This is a circuit that converts USB 3.1 to NVMe. It's used to transfer all data and the operating system from the computer to a larger capacity SSD. |
Notes:
(1): USB Type-C Port: This is where the converter circuit connects to the computer or other devices via a USB C 3.1 cable.
(2): Control Chip: The large chip in the middle of the circuit plays a key role in converting signals between USB and NVMe. (NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a high-speed storage protocol and interface designed specifically for SSDs using NAND flash memory. It allows faster data transfer between the SSD and the computer's CPU (central processing unit).
(3): Other Components: Surrounding the circuit board are components like capacitors (C), resistors (R), and inductors (L). These components help stabilize voltage and signals on the circuit.
(4): Connector for NVMe SSD. This is where the NVMe memory card plugs in so the circuit can convert the signals from this drive to the USB port for data reading/writing.
This circuit board is often used in storage devices, serving as an adapter to connect NVMe hard drives to a computer via USB, providing the high transfer speeds of NVMe through the USB 3.1 interface.
 |
This image illustrates how to use an NVMe SSD as an external storage device with the converter board and USB-C cable. |
Here are some related questions and useful answers:
- What is SATA?
SATA is a way to connect hard drives to computers, similar to a road for data to travel. While not as fast as NVMe, it is suitable for large storage at a reasonable cost and remains very popular in today’s computers.
So, in summary about NVMe and SATA:
- NVMe: Much faster but more expensive, suitable for high-performance applications like gaming, running heavy applications, or booting the operating system.
- SATA: Slower but cheaper, suitable for storing data that doesn't require high speed, like videos, photos, and backups.
To upgrade the SSD for a computer from 512GB to 1TB, you can refer to the following steps:
Step 1: Check the type of current SSD and the slots in your computer.
Identify the type of SSD you are using: Your computer may be using either SATA or NVMe SSD. Check the type of SSD by:
- Opening the computer and checking directly on the hard drive (clearly labeled as SATA or NVMe).
- Using software like CrystalDiskInfo or Speccy to check hardware specifications.
- Identify the SSD slot: Check if the computer has an M.2 slot (for NVMe SSD) or SATA port (for SATA SSD). Modern computers often have both slots, but make sure before buying a new drive.
Step 2: Purchase a new 1TB SSD.
Choose an NVMe or SATA 1TB SSD that fits your slot.
Some popular SSD brands include Samsung, WD (Western Digital).
Step 3: Backup your data.
Back up data from the old drive before replacing it to avoid losing important information.
You can back up using:
- An external hard drive or USB drive.
- Cloud storage services like Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive.
Step 4: Clone data from the old drive to the new one (if needed).
If you want to keep the operating system and data from the old 512GB drive to the new 1TB drive, you can clone (copy) all the data.
Software for cloning SSDs includes:
- Macrium Reflect (free).
- Acronis True Image (usually comes with the purchase of a new SSD).
My colleague used the Samsung Magician app that came with the SSD to copy all data from the old 512GB to the new 1TB.
Connect the new SSD via a SATA/USB converter case or NVMe/USB case to perform the data transfer (we used an NVMe/USB case as shown in the photo above).
Step 5: Replace the old SSD with the new SSD.
Turn off the computer and unplug it before opening.
Remove the old SSD from the SATA or M.2 slot.
Insert the new SSD into the correct slot, carefully replace the cover, and screw it tight.
If you're using a laptop, you may need to open the bottom of the device to access the hard drive.
Step 6: Set up the computer again (if you didn’t clone the data).
If you didn't clone the data and want to set it up from scratch:
- Create a USB installation for the operating system (Windows 10, 11, or Linux) using the Windows Media Creation Tool or other USB boot software.
- Reinstall the operating system on the new SSD.
Step 7: Check and enjoy the new storage.
Start the computer and check if the 1TB drive is recognized properly.
You can check the new drive’s capacity in This PC or Disk Management on Windows.
👶 Here are a few beginner questions and useful answers I found!
- Is SSD internal memory?
👉 SSD (Solid State Drive) can be either internal or external memory, depending on how it's used:
- Internal SSD: When installed inside a computer or laptop (usually in M.2 or SATA form), the SSD acts as the primary storage device. It contains the operating system, software, and user files. In this case, the SSD is considered internal memory because it's a fixed part of the system.
- External SSD: If the SSD is placed in an external case and connected to a computer via USB or Thunderbolt, it becomes a portable external hard drive. At this point, the SSD serves as external memory, easily movable between different devices.
In summary, SSD can be either internal or external memory depending on whether it is permanently installed inside the system or used as a portable hard drive.
- What is RAM capacity, and how does it compare to SSD?
👉 RAM (Random Access Memory) measures the temporary data storage capacity of RAM in a device. Measured in GB (gigabytes), the larger the RAM capacity, the more temporary data the computer can store and access during processing. RAM helps the computer run more smoothly when opening multiple programs or handling heavy tasks.
When should you upgrade RAM or SSD?
- Upgrade RAM when you feel the computer is slow when opening multiple programs simultaneously, or when running heavy applications like graphics, programming, or gaming.
- Upgrade SSD when you want to reduce boot time, speed up application launches, or need more storage space.
For example, when you start the computer, SSD will help boot faster because it has a faster read/write speed compared to HDD.
When you open many tabs in a browser or run multiple software simultaneously, RAM will determine whether the programs run smoothly, as it stores the temporary data of those programs.
In summary, RAM and SSD have different roles in a computer, and both are essential for ensuring fast and efficient operation.
👶 What is temporary data storage?
👉 Temporary data storage refers to retaining information and data that the computer or device needs to access quickly for ongoing tasks within a short timeframe. When these tasks end or when the computer is powered off, this temporary data is erased.
Role of temporary data storage:
Temporary data helps computers perform tasks faster and more efficiently. Some examples of temporary data storage include:
RAM (Random Access Memory): RAM stores temporary data for running programs and applications on the computer. For example, when you open software, its data will load from storage (SSD or HDD) into RAM so that the CPU can access and process it faster. When you close the software or turn off the machine, that data disappears from RAM. (I often download PDF eBooks that will store on SSD, but when I bookmark it in Edge, each time I access Edge, I will open directly from there, and the content of the book will open on the page I was reading).
CPU Cache: This is another form of temporary storage located near the processor (CPU) that allows extremely fast access to frequently used data. The cache stores commands or data that the CPU needs to retrieve continuously, reducing wait times.
Example of working with documents: When you open a Word document, its data is loaded from the hard drive into RAM so you can edit it quickly. When you save the document, it gets written back to storage (SSD or HDD). If you haven’t saved the document and turn off the computer, the temporary data in RAM will be lost, and you will lose any unsaved changes.
When gaming: The game data, such as images, sounds, and scenes, will load from storage into RAM. This helps the game run smoothly and faster. When you exit the game, this temporary data will be erased from RAM.
Why is temporary data necessary?
- Speed: Storing temporary data in RAM or cache allows computers to access and process data much faster than retrieving it from hard drives.
- Efficiency: Temporary storage enables the system to respond immediately to user tasks, such as opening applications, editing documents, or playing games.



Comments